
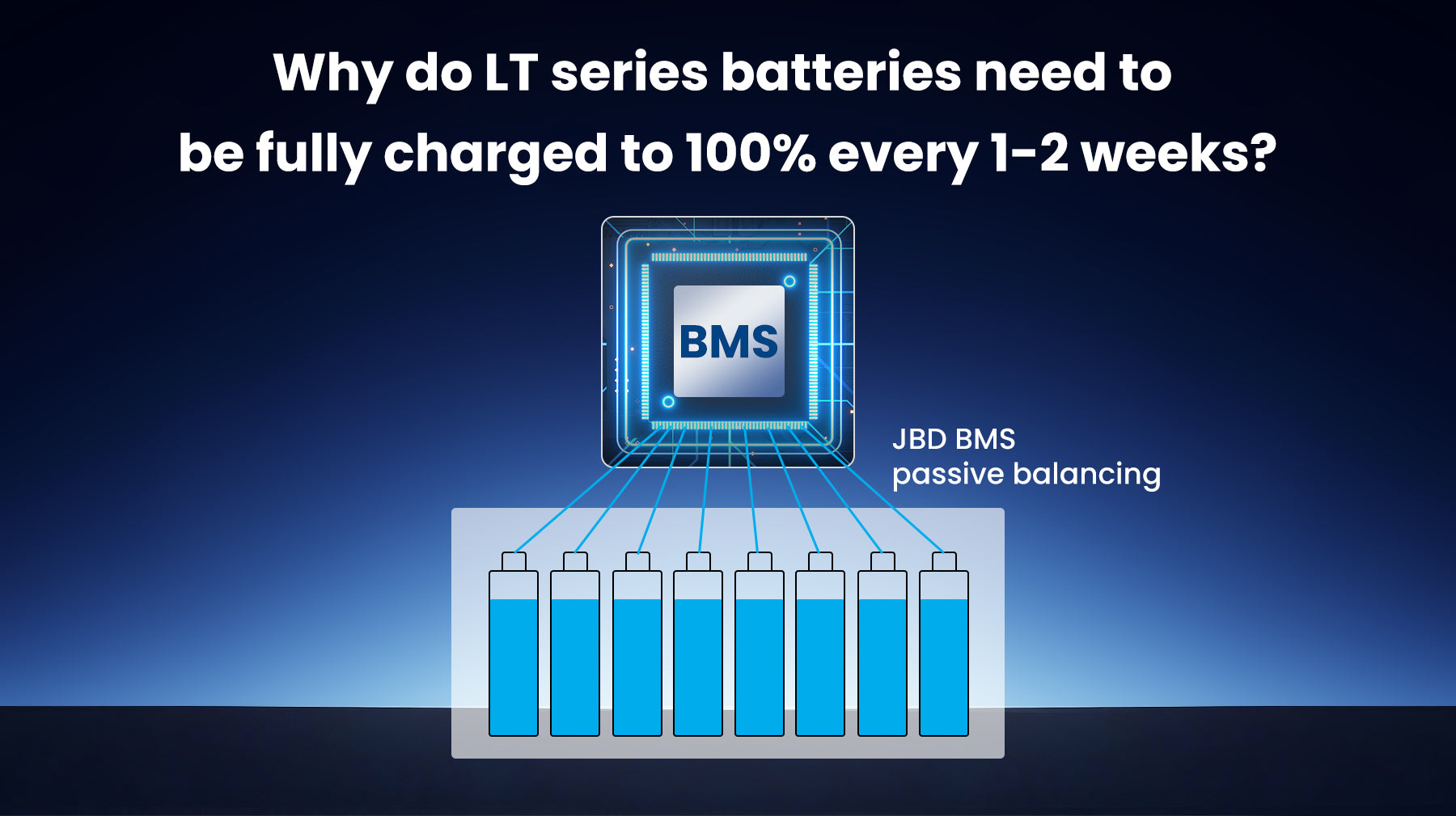
Novaic LT series batteries use the JBD battery management system. For batteries managed by the JBD BMS, some users may hear the recommendation to fully charge the battery to 100% every week. This recommendation has specific reasons, mainly involving the following aspects:
Battery Balancing: To ensure the voltages of the individual cells in the battery pack are consistent, preventing performance degradation caused by imbalances.
System Calibration: To help the BMS recalibrate the battery's charging state, ensuring accurate battery level indication.
JBD's BMS (Battery Management System) uses passive balancing and follows a calibration principle that primarily focuses on ensuring accurate battery performance and enhancing battery longevity. Here's a breakdown of how these mechanisms work:
1. Passive Balancing
The Active Balancing and Passive Balancing are two technologies used in Battery Management Systems (BMS) to maintain the balance of a battery pack. Their working principles differ:
Passive Balancing: In a battery pack, there may be differences in the charge between individual battery cells. Passive balancing works by "consuming" the excess charge from the higher-voltage cells, usually by converting it into heat through a resistor.
Active Balancing: Active balancing technology works by transferring the excess energy between battery cells to the lower-voltage cells instead of wasting it. This maximizes energy utilization efficiency. (Novaic GR series Batteries use active balancing BMS.)
2. Calibration Principle
The calibration principle in JBD's BMS refers to the process of recalibrating the state of charge (SOC) and the state of health (SOH) of the battery pack to ensure accurate battery management and performance tracking.
Key Aspects of the Calibration Process:
Recalibrating SOC (State of Charge): SOC represents the remaining charge in a battery, expressed as a percentage. Over time, the battery management system can lose track of the actual charge level due to small imbalances in the battery cells. Recalibration ensures that the BMS can accurately measure and report the SOC, which is crucial for determining the remaining runtime of the device or vehicle.
Recalibrating SOH (State of Health): SOH refers to the overall condition of the battery, including its capacity to hold a charge. As batteries age, their capacity gradually declines, and recalibrating SOH allows the system to account for changes in the battery’s performance, providing a more accurate estimation of remaining useful life.
Regular Calibration: For optimal battery management, recalibrating the battery regularly (especially charging it fully to 100%) ensures that the system's measurements stay accurate, and it can make necessary adjustments to prevent overcharging or overdischarging.
3. Why Charge to 100% for Calibration
JBD recommends charging the battery to 100% periodically, as this ensures the BMS can properly recalibrate the state of charge and state of health indicators:
Complete Charge Cycle: Charging the battery to 100% allows the BMS to perform full-scale balancing and recalibrate the SOC, ensuring that the voltage of all cells is uniform and that the system can accurately predict battery performance.
Recalibration of Voltage and SOC: A full charge (100%) helps the system measure the voltage at the top end, ensuring that it can detect any voltage imbalances and make necessary corrections. This is especially important for maintaining the health of the battery pack over its lifecycle.
4. Why Regular Calibration is Important
While passive balancing and recalibration of SOC/SOH can be done periodically, regular full charges help prevent long-term damage from occurring due to cell imbalance or incorrect SOC measurements.
Benefits of Regular Calibration:
Improved Battery Accuracy: Ensures the BMS accurately tracks the battery’s charge level, providing more reliable readings and longer-lasting performance.
Increased Battery Lifespan: Proper calibration helps prevent damage from overcharging or deep discharging, leading to a longer overall battery lifespan.
Better System Control: Accurate SOC and SOH readings allow the BMS to better manage the charging and discharging processes, optimizing the performance of the battery and connected devices.
5. Summary
JBD BMS's passive balancing helps ensure that the voltage across individual battery cells is even, which promotes safety and improves battery longevity. The calibration principle recalibrates the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) to ensure accurate battery performance and system control. Regularly charging the battery to 100% allows the BMS to recalibrate the battery’s SOC and maintain its accuracy, helping to prevent long-term imbalances, ensuring the battery’s optimal performance, and enhancing its lifespan.
This process is essential for maintaining the health of the battery pack, especially in high-demand applications like electric vehicles, solar storage systems, or electric bikes where precision and reliability are critical for long-term use.







Share:
How To Test a Deep Cycle Battery With a Multimeter